Introduction
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is an important concept within the field of psychology, contributing to our understanding of human motivation, behavior, and the factors that promote psychological well-being.
Understanding what motivates us as human beings is a complex yet intriguing subject. One prominent theory that attempts to shed light on this matter is Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Developed in the 1940s, Maslow’s theory postulates that human motivation is driven by a series of fundamental needs, organized in a hierarchical structure. By comprehending this framework, we gain valuable insights into what motivates individuals and how we can fulfill these needs. In this article, we will explore Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, delve into its components, and provide real-life examples to grasp its significance in our lives.
The Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs comprises five levels that outline the various needs that humans strive to satisfy. These levels are arranged in a pyramid, with the most basic needs at the bottom and the higher-level needs at the top. As individuals progress through the hierarchy, they gradually pursue more complex and abstract goals.
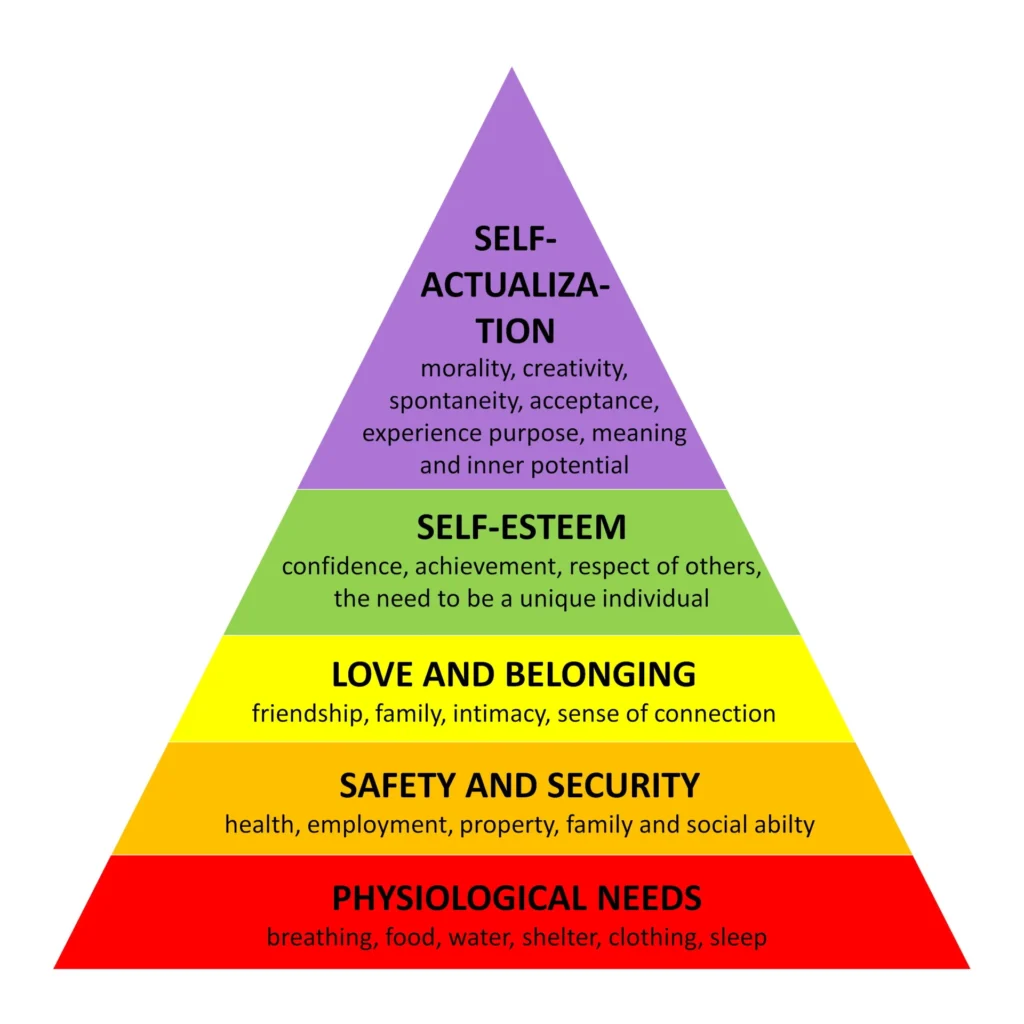
- Physiological Needs: At the foundation of the pyramid lie the physiological needs, which are essential for our survival. These include basic biological requirements such as air, water, food, sleep, and shelter. Without fulfilling these needs, individuals cannot progress to higher levels of motivation. For instance, a person who is hungry and thirsty will prioritize finding food and water before focusing on any other aspirations.
- Safety Needs: Once physiological needs are met, safety needs become a primary concern. These encompass the need for physical security, stability, protection from harm, and an environment that promotes well-being. Examples of safety needs being fulfilled are finding a secure place to live, having a stable job, and having access to healthcare.
- Love and Belongingness Needs: The third level of the hierarchy pertains to the need for love, affection, and a sense of belonging. Humans are inherently social creatures and strive to establish meaningful relationships, both romantic and platonic. Satisfying love and belongingness needs can occur through familial ties, friendships, and membership in social or professional groups. This level of motivation highlights the importance of human connections and the positive impact they have on our overall well-being.
- Esteem Needs: Moving up the pyramid, esteem needs encompass both external and internal factors that contribute to our self-esteem and self-worth. External sources of esteem include recognition, respect, and status, while internal sources comprise self-confidence, achievement, and personal growth. Fulfilling these needs involves gaining recognition for accomplishments, receiving praise, and feeling a sense of competence and confidence.
- Self-Actualization Needs: At the pinnacle of Maslow’s Hierarchy lies self-actualization, representing the highest level of human motivation. Self-actualization refers to the desire for personal growth, fulfillment of one’s potential, and a deep sense of purpose. Individuals pursuing self-actualization often engage in creative endeavors, seek personal development, and strive to make a meaningful impact on the world.
Understanding the Significance
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs provides a valuable framework for understanding human motivation and behavior. It emphasizes that individuals must first fulfill their lower-level needs before progressing to higher levels. For instance, it is challenging to focus on self-actualization if one is struggling to meet basic physiological needs.
Furthermore, the hierarchy recognizes that not everyone progresses through the levels at the same pace or reaches the highest level. Different individuals have varying degrees of motivation and prioritize different needs. Cultural and societal factors also influence the importance assigned to each level, as societal norms and values shape individuals’ aspirations.
Here are some key points that highlight its significance in detail:
- Understanding Human Needs: Maslow’s hierarchy provides a structured framework to comprehend the diverse range of needs that drive human behavior. It helps us recognize that motivation is not solely based on external rewards or incentives but is deeply rooted in fulfilling fundamental human needs.
- Prioritizing Needs: The hierarchy emphasizes the importance of satisfying lower-level needs before progressing to higher levels. This understanding is valuable in various contexts, such as personal development, education, and organizational management. It allows individuals and institutions to identify and address the most critical needs at each level, ensuring a solid foundation for growth and progress.
- Individual Differences: Maslow’s theory acknowledges that individuals may have different priorities and progress through the hierarchy at different rates. This recognition highlights the need for personalized approaches in understanding and meeting the unique needs of each person. It encourages us to consider factors such as culture, upbringing, and personal values when assessing an individual’s motivations.
- Creating Supportive Environments: The hierarchy helps in creating environments that promote well-being and motivation. By understanding the various levels of needs, we can design settings that provide safety, foster social connections, and support personal growth. For example, organizations can prioritize creating a positive work culture that addresses employees’ physiological and safety needs while also providing opportunities for recognition and self-development.
- Self-Reflection and Personal Growth: Maslow’s theory prompts individuals to reflect on their own needs and motivations. By evaluating which needs are fulfilled and which ones require attention, individuals can identify areas for personal growth and take steps towards self-actualization. It encourages introspection and self-awareness, leading to greater personal fulfillment and a sense of purpose.
- Holistic Approach: The hierarchy encompasses both physical and psychological needs, offering a holistic view of human well-being. It recognizes that individuals are not solely driven by material or external factors but also seek emotional connection, self-esteem, and personal fulfillment. This holistic approach reminds us of the importance of addressing multiple dimensions of human existence to achieve a balanced and meaningful life.
- Application in Various Fields: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs finds application in diverse fields such as psychology, education, marketing, leadership, and personal development. It provides a common language and conceptual framework that professionals can utilize to understand and address human motivation effectively.
Conclusion
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs offers a comprehensive framework to comprehend what motivates human behavior. By understanding and addressing these needs, we can create environments that foster personal growth, well-being, and fulfillment. The hierarchy reminds us of the essential nature of basic physiological requirements, the significance of safety and security, the power of social connections, the role of recognition and self-esteem, and the potential for self-actualization.
By recognizing and respecting the diverse needs of individuals, we can better support one another in our pursuit of a meaningful and fulfilling life.

[…] https://amateurs.co.in/what-is-maslows-hierarchy-of-needs/ […]
[…] https://amateurs.co.in/what-is-maslows-hierarchy-of-needs/ […]
[…] and unknowable delves into the philosophical and practical understanding of human capabilities. This concept acknowledges the complexity, variability, and unpredictability inherent in each individ… In exploring this theme, we must consider the multifaceted nature of potential, the limitations of […]